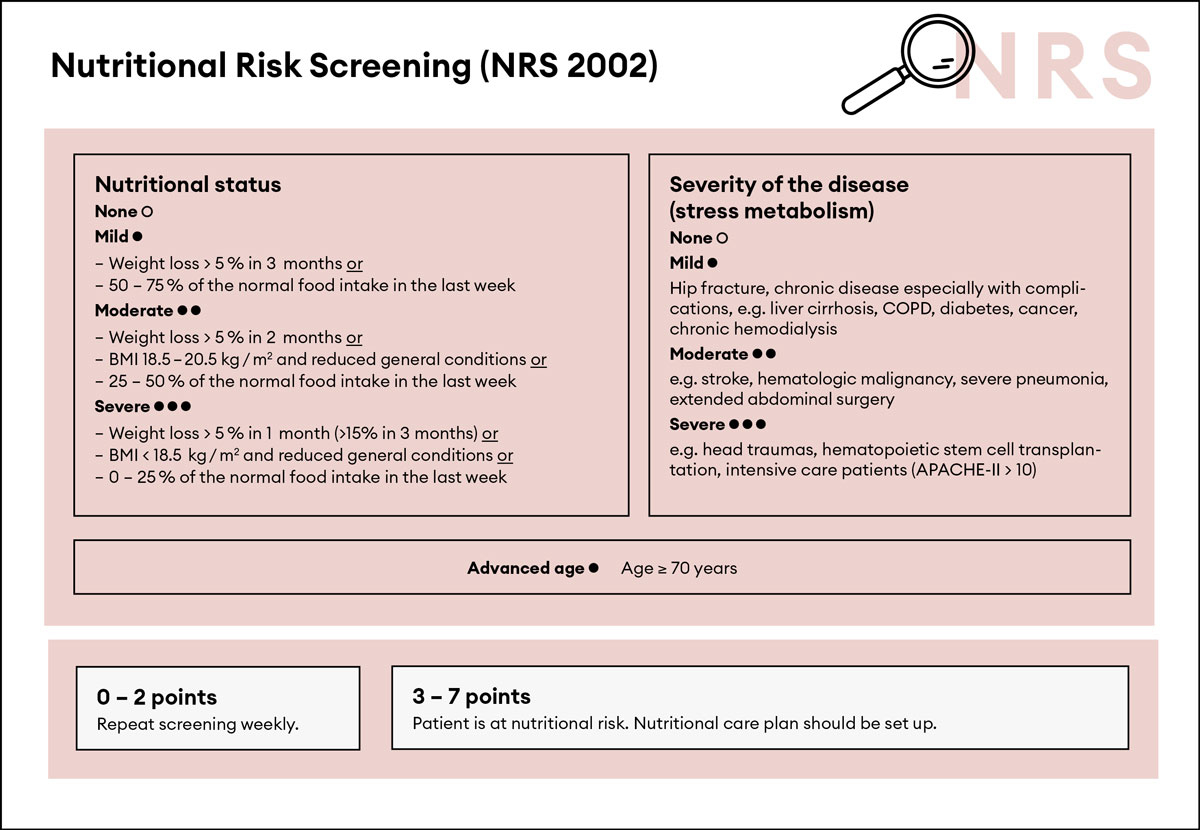
Figure 1 NRS 2002, adapted from Kondrup et al. [13] with permission from Elsevier.
BMI = body mass index; COPD = chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; APACHE-II = APACHE-II Score
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4414/smw.2020.20204
Hippocrates, one of the founders of medicine as a scientifically orientated profession, had already considered nutrition as a major factor to help cure diseases. The significance of nutrition in clinical practice, however, has never quite fulfilled those expectations [1, 2]. Many physicians still do not consider nutrition as a medical treatment but rather as a supportive treatment [3]. As recent trials demonstrated that early, individualised nutritional support improves clinical outcomes of patients, it is now time for a paradigm shift [4–7]. We must now think of clinical nutrition as a medical treatment that, by decreasing metabolic stress responses, preventing apoptosis, reducing oxidative stress in other organs and modulation of the body’s immune response, has a measurable impact on disease development and recovery [8, 9]. This is particularly true for patients with malnutrition, a condition that has been associated with increased risks of adverse clinical outcomes [10]. In such patients, a nutritional strategy needs to be established in order to provide optimal nutritional support. There are three basic prerequisites:
This review article provides an example of a nutritional support strategy and discusses basic principles of nutritional therapy for medical inpatients. The nutritional support interventions discussed are mainly based on consensus guidelines issued by the European Society of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN) [11]. As the underlying evidence, however, is variable in quality and reliability, some of the recommendations are supported only by expert opinions and may need to be adapted once new evidence becomes available.
Interdisciplinary as well as multiprofessional support and shared decision making is needed for optimal nutritional care [12]. Appropriate duties and responsibilities must be assigned in order to ensure that each involved profession can provide important contributions. Interdisciplinary communication should be integrated into daily routine on the ward. Responsibilities may be shared as follows:
Screening for malnutrition should be performed at the time of patient admission to the medical ward or at least within the first 24–48 hours. The use of a validated screening tool for nutritional risk is recommended; for example, the Nutritional Risk Screening 2002 (NRS 2002) or the Mini Nutritional Assessment short form (NMA-sf) [11, 13, 14]. Several recent studies have used the NRS 2002 and provided evidence that this score has strong prognostic implications and identifies patients who benefit from nutritional support interventions [6, 9, 15, 16]. The NRS 2002 (see fig. 1) includes an assessment of the patient’s nutritional status (based on weight loss, body mass index [BMI] and general condition or food intake) as well as disease severity (stress metabolism), and indicates any increased risk of adverse outcomes [13]. Each risk predictor is scored from 0 to 3 points and patients receive 1 extra point if they are aged 70 years or older [13].

Figure 1 NRS 2002, adapted from Kondrup et al. [13] with permission from Elsevier.
BMI = body mass index; COPD = chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; APACHE-II = APACHE-II Score
If the screening test is positive, a more detailed assessment of nutritional status is recommended. Table 1 gives an overview of anthropometric and laboratory parameters useful for baseline examination of a patient at risk. In some cases of severe or chronic malnutrition, there may be a need for additional diagnostic studies (e.g., if pancytopenia is present). These patients may benefit from the involvement of an experienced specialist in malnutrition.
Table 1 Basic assessment at admission.
| Parameter | Significance and implications |
|---|---|
| NRS 2002 | Screening for malnutrition |
| Iron, holotranscobalamin, folic acid in erythrocytes | Diagnostic assessment of anaemia. Substitution in the case of deficiency |
| Electrolytes (sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, phosphate) | Screening for deficiency and assessing risk for refeeding syndrome. Substitution according to the cited consensus paper by Friedli et al., Nutrition, 2018 [28]. |
| Creatinine | Baseline assessment of renal function. Possible sign for low muscle mass if low |
| Liver function tests | Baseline assessment of hepatic status |
| International normalised ratio | Indication of vitamin K deficiency, if low. Substitution if clinically indicated. Caveat elevated/reduced by coumarins and direct-acting oral anticoagulants. |
| Vitamin D | Baseline assessment because of frequent deficiency and frequent association of osteoporosis in malnutrition. Substitution in the case of deficiency |
If malnutrition is manifest or presents an imminent risk, an individualised nutritional support strategy should be established within 48 hours after hospital admission. In a first step, a trained dietician should calculate individual goals for daily energy and protein requirements for each patient. Details on establishing individual nutritional objectives will be discussed in the following text. We recommend introducing a nutritional care plan flow chart system to guide further management, achieve individual nutritional goals and assure decision-making consistency within the hospital. Figure 2 presents a pragmatic algorithm for nutritional management of patients (adapted from the EFFORT trial [15]).
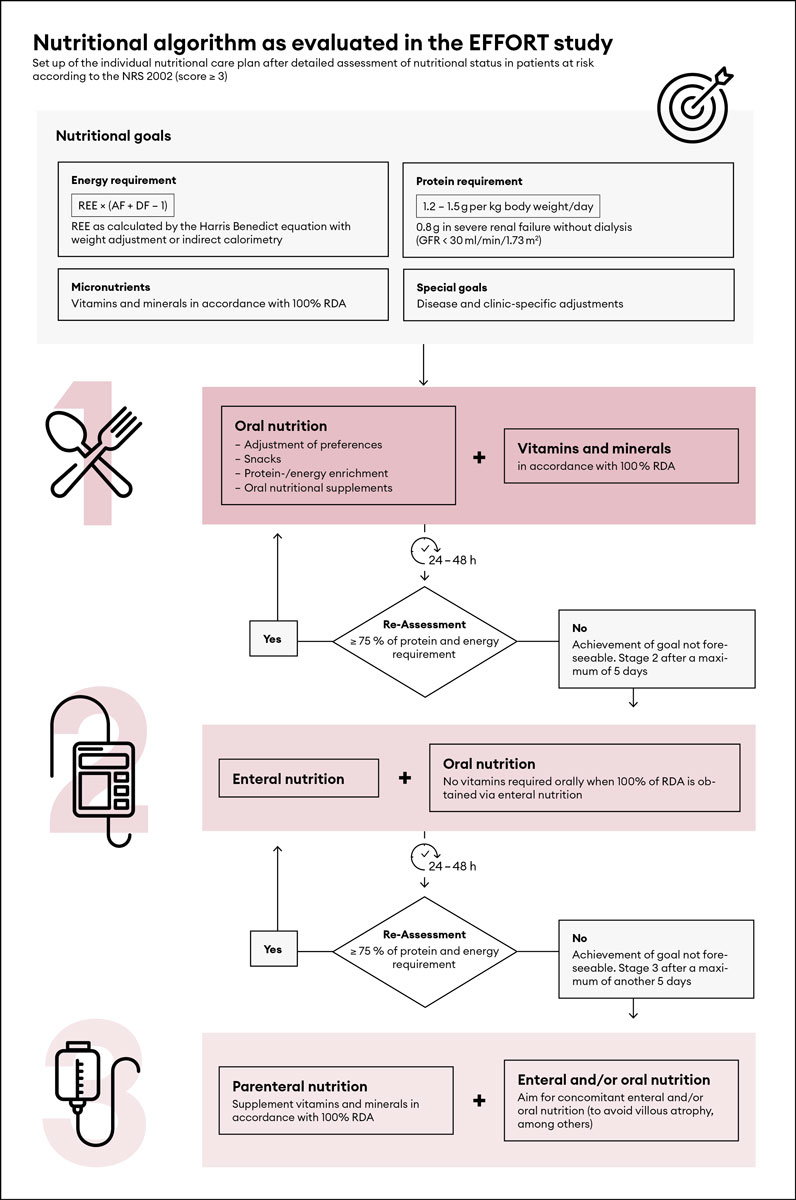
Figure 2 Algorithm flow chart for nutritional support in medical inpatients, adapted from Bounoure et al. [17] with permission from Elsevier.
REE = resting energy expenditure; AF = activity factor; DF = disease factor; RDA = recommended daily allowance; GFR = glomerular filtration rate
Terms and abbreviations:
The formula of TEE is based on the energy balance of healthy probands. Diseases affect energy requirements by their impact on metabolic processes, in particular by increasing catabolism. Therefore for patients, the general formula has to be further adjusted by adding a disease-specific factor. Disease-specific factors range between 5 and 50% of the REE.
There is not one single validated method to estimate energy requirements [11]. The gold standard to estimate energy needs is indirect calorimetry, which is, however, time consuming, resource intensive and technically complex [18]. REE also varies according to the severity of the illness (hypermetabolism). Repeated measurements would have to be taken in order to ensure continuity. As a result of these factors, energy needs are in clinical routine often estimated using equations based on the calculation of resting metabolic rates. There is a multitude of evaluated prediction equations using sex, weight, height and age (e.g., Harris-Benedict-Formula 1919, FAO/WHO/UNU 1985, Mifflin-St Jeor 1990) or simple weight-based formulae (e.g., 25–30 kcal / kg bodyweight / day; BASA-ROT-Table) [11, 19, 20]. Most of these equations provide good estimates for groups of patients but show significant imprecision in individual cases; which can lead to both over- and underestimation of energy expenditure [19]. It is therefore recommended to use a tool that is easier to implement but still reliable in clinical practice. Estimates of energy expenditure are helpful to define a starting point but need adaptation during the course of the hospitalisation. In the case of uncertainty, additional indirect calorimetry may be performed [11].
Recommendations for weight-based formulae according to ESPEN guidelines are [11]:
Overall, there are few studies assessing the effect of different amounts of protein intake on outcome. Some clinical data suggest that a protein intake of >1 g / kg bodyweight / day appears to reduce the risk of complications and weight loss [21]. In terms of clinical and functional outcome, older and polymorbid patients may benefit from a higher protein intake, for example 1.5–2 g / kg bodyweight / day [17, 22]. Also, a daily protein intake of 1.2–1.5 g / kg bodyweight to adjust for targets for patients suffering from acute renal failure (0·8 g / kg bodyweight / day) [11, 17, 24].
There are several uncertainties regarding the optimal use of proteins in clinical nutrition. First, there is uncertainty whether calculations of protein requirements should use actual or ideal body weight as their reference [25]. This is relevant particularly in obese patients, where protein goals calculated from the actual body weight result in very high quantities and often are difficult to reach. Based on pathophysiological considerations, calculating protein needs according to ideal body weight should provide adequate quantities and should be preferred in clinical practice [26]. However, so far, there is no evidence supporting this assumption. Second, in addition to protein quantity, it remains largely unknown which type of protein has most beneficial effects on patient outcomes.
Malnourished patients are at risk for micronutrient deficiency as a result of decreased intake or increased requirements [11]. Thus, screening for micronutrient deficiencies such as iron, vitamin B12, folic acid and vitamin D are recommended. According to patient history and clinical presentation, in particular in cases of severe or chronic malnutrition, more comprehensive screening including vitamin B1, vitamin B6, vitamin A, vitamin E, vitamin C, zinc and selenium, as well as the international normalised ratio (INR) or Quick test as an indirect measure of vitamin K should be considered. Analytic prerequisites for all laboratory parameters, in particular for vitamin E, should be followed carefully in order to ensure reliable results.
Cases of general vitamin depletion are also at increased risk for serious trace element deficiency. In absence of specific toxicity risks or known micronutrient adequacy, supplements should cover both, ideally in a multivitamin/multi-trace-element formula [11]. The recommended daily intake may temporarily be exceeded in order to replace depleted stores [11]. General prescription of a multivitamin/multi-trace-element supplement does not seem to be cost-effective but, depending on circumstances, it might be reasonable to prescribe one to prevent recurrent multivitamin/multi-trace-element deficiency after repletion and/or in the presence of persisting risk factors for malnutrition [27]. Particularly in patients at risk for refeeding syndrome, careful monitoring and substitution of vitamins and micronutrients is important [28, 29].
Multiple new formulas with potential immune-modulating capacities are currently gaining attention for use in specific patient populations, particularly in intensive care units and surgical wards. To-date there is no strong evidence for their beneficial influence on clinical outcome in medical or polymorbid non-critically ill patients [11].
According to a randomised controlled trial by Wong et al., wound healing might be improved by adding a combination of amino acids (β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate [βHMB], glutamine and arginine) to a hypermetabolic diet (energy goals 30–35 kcal / kg bodyweight / day) in patients with pressure ulcers [30].
Fibre supplementation has been recommended to improve bowel function and feeding tolerance and reduce diarrhoea with enteral nutrition [31]. Although the pathogenesis of diarrhoea in patients receiving enteral nutrition in most cases is multifactorial, the fibre content of enteral formulas might be one of the relevant factors. Fibre content also influences clinical parameters such as gastrointestinal transit time, bowel frequency and daily stool wet weights [32, 33]. In an attempt to prevent diarrhoea, the fibre content of enteral formulas has been adapted to better reflect the fibre content of normal food. Results have so far been inconclusive, with heterogeneity among study protocols in terms of fibre type, blended versus single fibre source and dose of fibre content. This heterogeneity may be explained by the dependence of gastrointestinal effects on fibres solubility in water and fermentability by the microbiota. Still, according to a recent meta-analysis formulas containing fibre may reduce risk of diarrhoea as compared with fibre-free formulas particularly in non-critically ill medical patients [32]. One randomised controlled trial included in the meta-analysis, which focused on elderly non-critically ill patients with relevant protein malnutrition, came to a conclusion similar to the overall conclusion by Elia et al. [31, 32]. Additionally, formulas containing a blend of soluble and insoluble fibres resulted in better gastrointestinal tolerance and reduced diarrhoea in comparison with single source fibre [33]. Further, formulas predominantly containing partially hydrolysed guar gum as their source of soluble fibre seem to be better than other fibre types in the prevention of diarrhoea. Hence, it is recommended to use an enteral nutrition formula enriched with a mix of soluble and insoluble fibres, particularly in patients receiving enteral nutrition and experiencing diarrhoea.
In general, electrolyte-free fluid requirements of adults range from about 1500–2000 ml or 25–30 ml / kg bodyweight / day for routine maintenance of fluid balance [36, 37]. Particularly in older patients, fluid needs should be closely monitored in order to ensure that minimum goals are met regularly [37]. During the course of the hospitalisation fluid supplementation should be re-evaluated daily. An appropriate re-evaluation takes several parameters into account: electrolytes, particularly sodium, clinical fluid balance, oral intake, fluid supply by enteral or parenteral nutrition, fluid losses and clinical circumstances such as inflammation.
Systematic screening of at-risk patients at the time of hospital admission for malnutrition using the NRS 2002 enables the nutritional care team to plan a thorough and rapid assessment of nutritional status, and concomitantly allows the establishment of nutritional support within the first 48 hours. It is important to note that outside critical care, there are few clinical studies comparing the effects of early with late start of nutritional intervention on clinical outcome. A randomised controlled trial by Heregova found less loss of lean body mass, as well as improved recovery to baseline lean body mass, in patients treated with early nutritional support and low intensity exercise [38]. In addition, the intervention group retained more independence for performing activities of daily living [38]. In intensive care settings, studies have suggested that early start of (over-)nutrition, particularly when parenteral nutrition is used, may have harmful effects [11]. Still, evidence from intensive care settings should not unconditionally be adopted on medical wards because of differences in underlying disease, extent of inflammation and resulting catabolism. Thus, for the medical inpatient, early start of nutritional support is recommended.
For a patient who tolerates oral nutrition, the paradigm “If the gut works, use it!” should be followed for both the intensive care setting and the medical ward. Several high-quality, randomised controlled trials in critical care settings favour enteral over parenteral nutrition owing to reduced risk of infectious and noninfectious complications [11]. For medical ward patients, a step-wise escalation of nutritional support should be made as follows.
The positive effect of oral nutritional supplements (ONSs) has been documented in several high-quality randomised controlled trials with medical inpatients. The effects included preservation of lean body mass and retained independence for activities of daily life, as well as reduced complications during hospitalisation and nonelective readmissions [21, 38–40]. ONSs did not negatively affect oral food intake and therefore did not disguise or inhibit increasing appetite of patients, particularly if given in between meals or in the evening [38].
Insufficient oral intake has been defined by the ESPEN as an oral intake ≤75% of the estimated daily energy needs [11]. The most frequent limiting factors for enteral nutrition in clinical practice are intolerance of the nasogastric tube, nausea and diarrhoea. Diarrhoea in particular may present a relevant problem. To improve gastrointestinal tolerance of enteral nutrition, we propose the following:
Parenteral nutrition is mainly indicated in patients not tolerating oral and enteral nutrition as a result of intestinal dysfunction and oral or enteral intake ≤75% of the estimated daily energy needs.
Discontinuation or de-escalation of nutritional support is recommended if gastrointestinal tolerance, appetite and oral intake improve. No significant suppression of appetite was seen in one high-quality randomised controlled trial on ONSs, but data on enteral and parenteral nutrition remain controversial [41].
We expect a partial reduction of appetite. In our own experience, the appetite-suppressing effect is lower in patients experiencing fast recovery or those ready to transition to the early rehabilitation phase.
Nutritional therapy should be withdrawn if ≥75% of recommended energy needs are met orally [11].
A regular evaluation of effects of nutritional therapy as well as screening for undesirable side effects are recommended during a nutritional therapy regimen.
Historically, albumin has been considered as one of the main nutritional laboratory parameters [42]. Yet its reliability is as a marker of malnutrition is limited. The interpretation of albumin levels is, among other reasons, mainly complicated by its long half-life of about 21 days and its property as a negative acute phase protein [43]. Pre-albumin, with a half-life of about 3 days, is a better marker of recent food intake, yet is often not available in routine laboratory testing and its interpretation remains challenging if a patient presents with inflammation. It is therefore not generally recommended to consider albumin as a nutritional parameter, nor is it recommended in the basic work-up of malnutrition. Exceptionally, it might complement an extensive malnutrition work-up in the hands of experienced clinicians.
Refeeding syndrome (RFS) is a condition resulting from an anabolic reaction caused by nutritional therapy and is associated with serum electrolyte shifts (mainly potassium, magnesium and phosphate), thiamine deficiency and clinical symptoms (e.g., oedema, tachypnoea, tachycardia) resulting from metabolic changes and an imbalance of fluids. The main trigger for RFS is a switch from a catabolic to an anabolic state, as a normal physiological reaction during the beginning of the replenishment phase [29]. In most cases, RFS appears within the first 3 days of initiating nutritional support [44]. It commonly occurs with all types of nutritional support, but the risk is higher in patients receiving enteral or parenteral nutrition [45]. Clinically, RFS may present as a mild form with almost no clinical signs and no risk to the patient, or as more severe forms causing clinical deterioration, including sudden cardiac death [46].
In patients with a high risk of developing RFS, daily monitoring of electrolytes is recommended, at least during the first 2–4 days following initiation of nutritional support or relevant dose adjustments of enteral and parenteral nutrition. Additionally, physical examination focusing on balance of fluids and a daily electrocardiogram in high-risk situations should be performed. RFS can be prevented by low levels of energy administration during the first phase of feeding and a slow progression of dose adjustments. Recently, a clinical practice guideline (consensus paper) has been published discussing risk assessment, prevention, treatment and monitoring of patients with RFS in more detail [28].
Until recently, interventional research proving that nutritional support improves clinical outcomes has been lacking. There have been several publications on the beneficial aspects of nutritional interventions, which showed improvement of nutritional parameters and quality of life, but did not evaluate the influence on overall survival [47]. Recent high-quality trials such as the NOURISH and the EFFORT trials have provided important new evidence linking nutritional support to better clinical outcomes in terms of reduction of mortality and severe complications, as well as functional outcomes and quality of life [48–50]. The results strongly support the systematic screening for malnutrition of medical inpatients followed by nutritional assessment and initiation of individualised nutritional support in patients at risk. These recommendations are also supported by a recent systematic review and meta-analysis demonstrating a 25% reduction in mortality and hospital readmission in patients receiving nutritional support [51]. It is now time to consider nutrition as a medical treatment to complement organ and disease-specific therapies.
Algorithm-guided clinical decision making for nutritional support is the backbone of an evidence-based nutritional strategy. It facilitates the management of individual patients on the ward, enables consistency of nutritional strategies within a clinic and improves harmonisation of nutritional strategies between clinics. This will potentially lead to enhanced comparability and better conditions for further research, which is urgently needed in order to maximise efficacy, minimise side effects and reduce the cost of nutritional support.
In-hospital management of nutritional therapy may also be combined with low-intensity resistance training to stimulate lean muscle growth. A meta-analysis of studies on progressive resistance training in older adults showed clear benefits and improved physical function [7, 52–54]. Study results showed that resistance exercise designed to reverse muscle loss and low muscle protein synthesis was as effective in older adults as it was in younger individuals [55]. The temporal correlation of protein ingestion relative to exercise may also support muscle mass regeneration. In a study of younger adult men, the benefits of resistance exercise on protein synthesis persisted up to 24 hours post-exercise and it should be considered, particularly in the out-patient setting [56]. More research is needed to delineate mechanisms which link physical activity and nutrition to recovery of lost muscle protein in older adults.
As recovery of lost lean body mass is more difficult and time-consuming than its preservation, early interventions aimed at prevention are important. In patients already experiencing significant muscle loss, nutritional therapy (as well as guided exercise during hospitalisation) might not be enough to rebuild muscle mass. Subsequent out-patient programmes to optimise nutritional status and encourage lean body mass gain could become part of the comprehensive management of malnourished patients in the near future. There are several small outpatient studies that demonstrated the benefit of βHMB on the build-up of lean muscle mass [57, 58]. These results, however, must be confirmed by larger trials before they can be accepted as general recommendations.
Finally, further personalisation of the above-mentioned general nutritional strategy will be necessary to maximise the effect of nutritional interventions and exercise. The term “personalised” highlights the fact that not all patients respond in the same way to medical interventions. Whether or not a patient benefits at any given point in time from nutritional therapy and exercise may be affected by illness-specific (e.g., comorbidities, inflammation, oxidative stress) or patient-specific factors (e.g., age, sex, genetic predisposition). The field of metabolomic research presents a promising new approach to personalise interventions based on metabolic clusters and specific patient phenotypes.
No financial support or other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article were reported.
1 Merker M , Gomes F , Stanga Z , Schuetz P . Evidence-based nutrition for the malnourished, hospitalised patient: one bite at a time. Swiss Med Wkly. 2019;149:w20112. doi:.https://doi.org/10.4414/smw.2019.20112
2 Schuetz P . “Eat your lunch!” - controversies in the nutrition of the acutely, non-critically ill medical inpatient. Swiss Med Wkly. 2015;145:w14132. doi:.https://doi.org/10.4414/smw.2015.14132
3 Schütz P , Bally M , Stanga Z , Keller U . Loss of appetite in acutely ill medical inpatients: physiological response or therapeutic target? Swiss Med Wkly. 2014;144:w13957. doi:.https://doi.org/10.4414/smw.2014.13957
4 Sobotka L . Basics in Clinical Nutrition: Nutritional support in different clinical situations. Clin Nutr. 2010;5(3):e153–4. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclnm.2009.06.015
5 Cederholm T , Bosaeus I , Barazzoni R , Bauer J , Van Gossum A , Klek S , et al. Diagnostic criteria for malnutrition - An ESPEN Consensus Statement. Clin Nutr. 2015;34(3):335–40. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2015.03.001
6 Felder S , Braun N , Stanga Z , Kulkarni P , Faessler L , Kutz A , et al. Unraveling the Link between Malnutrition and Adverse Clinical Outcomes: Association of Acute and Chronic Malnutrition Measures with Blood Biomarkers from Different Pathophysiological States. Ann Nutr Metab. 2016;68(3):164–72. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1159/000444096
7 Deutz NE , Matheson EM , Matarese LE , Luo M , Baggs GE , Nelson JL , et al.; NOURISH Study Group. Readmission and mortality in malnourished, older, hospitalized adults treated with a specialized oral nutritional supplement: A randomized clinical trial. Clin Nutr. 2016;35(1):18–26. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2015.12.010
8 Gomes F , Schuetz P , Bounoure L , Austin P , Ballesteros-Pomar M , Cederholm T , et al. ESPEN guidelines on nutritional support for polymorbid internal medicine patients. Clin Nutr. 2018;37(1):336–53. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2017.06.025
9 Felder S , Lechtenboehmer C , Bally M , Fehr R , Deiss M , Faessler L , et al. Association of nutritional risk and adverse medical outcomes across different medical inpatient populations. Nutrition. 2015;31(11-12):1385–93. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2015.06.007
10 Felder S , Lechtenboehmer C , Bally M , Fehr R , Deiss M , Faessler L , et al. Association of nutritional risk and adverse medical outcomes across different medical inpatient populations. Nutrition. 2015;31(11-12):1385–93. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2015.06.007
11 Gomes F , Schuetz P , Bounoure L , Austin P , Ballesteros-Pomar M , Cederholm T , et al. ESPEN guidelines on nutritional support for polymorbid internal medicine patients. Clin Nutr. 2018;37(1):336–53. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2017.06.025
12 Reber E , Gomes F , Bally L , Schuetz P , Stanga Z . Nutritional Management of Medical Inpatients. J Clin Med. 2019;8(8):1130. doi:.https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081130
13 Kondrup J , Allison SP , Elia M , Vellas B , Plauth M ; Educational and Clinical Practice Committee, European Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ESPEN). ESPEN guidelines for nutrition screening 2002. Clin Nutr. 2003;22(4):415–21. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-5614(03)00098-0
14 Reber E , Gomes F , Vasiloglou MF , Schuetz P , Stanga Z . Nutritional Risk Screening and Assessment. J Clin Med. 2019;8(7):1065. doi:.https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8071065
15 Schuetz P , Hausfater P , Amin D , Haubitz S , Fässler L , Grolimund E , et al. Optimizing triage and hospitalization in adult general medical emergency patients: the triage project. BMC Emerg Med. 2013;13(1):12. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-227X-13-12
16 Hersberger L , Bargetzi L , Bargetzi A , Tribolet P , Fehr R , Baechli V , et al. Nutritional risk screening (NRS 2002) is a strong and modifiable predictor risk score for short-term and long-term clinical outcomes: secondary analysis of a prospective randomised trial. Clin Nutr. 2019;S0261-5614(19)33171-1. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2019.11.041
17 Bounoure L , Gomes F , Stanga Z , Keller U , Meier R , Ballmer P , et al.; Members of the Working Group. Detection and treatment of medical inpatients with or at-risk of malnutrition: Suggested procedures based on validated guidelines. Nutrition. 2016;32(7-8):790–8. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2016.01.019
18 Branson RD , Johannigman JA . The measurement of energy expenditure. Nutr Clin Pract. 2004;19(6):622–36. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1177/0115426504019006622
19 Boullata J , Williams J , Cottrell F , Hudson L , Compher C . Accurate determination of energy needs in hospitalized patients. J Am Diet Assoc. 2007;107(3):393–401. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jada.2006.12.014
20 Valentini L , Roth E , Jadrna K , Postrach E , Schulzke JD . The BASA-ROT table: an arithmetic-hypothetical concept for easy BMI-, age-, and sex-adjusted bedside estimation of energy expenditure. Nutrition. 2012;28(7-8):773–8. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2011.11.020
21 Starke J , Schneider H , Alteheld B , Stehle P , Meier R . Short-term individual nutritional care as part of routine clinical setting improves outcome and quality of life in malnourished medical patients. Clin Nutr. 2011;30(2):194–201. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2010.07.021
22 McClave SA , DiBaise JK , Mullin GE , Martindale RG . ACG Clinical Guideline: Nutrition Therapy in the Adult Hospitalized Patient. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111(3):315–34, quiz 335. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2016.28
24 Cano N , Fiaccadori E , Tesinsky P , Toigo G , Druml W , Kuhlmann M , et al.; DGEM (German Society for Nutritional Medicine); ESPEN (European Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition). ESPEN Guidelines on Enteral Nutrition: Adult renal failure. Clin Nutr. 2006;25(2):295–310. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2006.01.023
25 Peterson CM , Thomas DM , Blackburn GL , Heymsfield SB . Universal equation for estimating ideal body weight and body weight at any BMI. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016;103(5):1197–203. doi:.https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.115.121178
26 Choban P , Dickerson R , Malone A , Worthington P , Compher C ; American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. A.S.P.E.N. Clinical guidelines: nutrition support of hospitalized adult patients with obesity. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2013;37(6):714–44. doi:.. Correction in: JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2015;39(6):998. doi:https://doi.org/10.1177/0148607113499374
27 Kilonzo MM , Vale LD , Cook JA , Milne AC , Stephen AI , Avenell A ; MAVIS Trial Group. A cost-utility analysis of multivitamin and multimineral supplements in men and women aged 65 years and over. Clin Nutr. 2007;26(3):364–70. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2006.11.002
28 Friedli N , Stanga Z , Culkin A , Crook M , Laviano A , Sobotka L , et al. Management and prevention of refeeding syndrome in medical inpatients: An evidence-based and consensus-supported algorithm. Nutrition. 2018;47:13–20. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2017.09.007
29 Friedli N , Stanga Z , Sobotka L , Culkin A , Kondrup J , Laviano A , et al. Revisiting the refeeding syndrome: Results of a systematic review. Nutrition. 2017;35:151–60. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2016.05.016
30 Wong A , Chew A , Wang CM , Ong L , Zhang SH , Young S . The use of a specialised amino acid mixture for pressure ulcers: a placebo-controlled trial. J Wound Care. 2014;23(5):259–60, 262–4, 266–9. doi:.https://doi.org/10.12968/jowc.2014.23.5.259
31 Vandewoude MFJ , Paridaens KMJ , Suy RAL , Boone MAA , Strobbe H . Fibre-supplemented tube feeding in the hospitalised elderly. Age Ageing. 2005;34(2):120–4. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afh242
32 Elia M , Engfer MB , Green CJ , Silk DB . Systematic review and meta-analysis: the clinical and physiological effects of fibre-containing enteral formulae. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;27(2):120–45. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2007.03544.x
33 Whelan K , Schneider SM . Mechanisms, prevention, and management of diarrhea in enteral nutrition. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2011;27(2):152–9. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1097/MOG.0b013e32834353cb
36National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Guidance. Intravenous Fluid Therapy: Intravenous Fluid Therapy in Adults in Hospital. London: Royal College of Physicians (UK) National Clinical Guideline Centre; 2013.
37 Volkert D , Beck AM , Cederholm T , Cruz-Jentoft A , Goisser S , Hooper L , et al. ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition and hydration in geriatrics. Clin Nutr. 2019;38(1):10–47. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2018.05.024
38 Hegerová P , Dědková Z , Sobotka L . Early nutritional support and physiotherapy improved long-term self-sufficiency in acutely ill older patients. Nutrition. 2015;31(1):166–70. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2014.07.010
39 Gariballa S , Forster S , Walters S , Powers H . A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of nutritional supplementation during acute illness. Am J Med. 2006;119(8):693–9. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2005.12.006
40 Mendenhall CL , Moritz TE , Roselle GA , Morgan TR , Nemchausky BA , Tamburro CH , et al. Protein energy malnutrition in severe alcoholic hepatitis: diagnosis and response to treatment. The VA Cooperative Study Group #275. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1995;19(4):258–65. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1177/0148607195019004258
41 Stratton R . The impact of nutritional support on appetite and food intake. Clin Nutr. 2001;20:147–52. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1054/clnu.2001.0416
42 Fuhrman MP . The albumin-nutrition connection: separating myth from fact. Nutrition. 2002;18(2):199–200. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/S0899-9007(01)00729-8
43 Eckart A , Struja T , Kutz A , Baumgartner A , Baumgartner T , Zurfluh S , et al. Relationship of nutritional status, inflammation, and serum albumin levels during acute illness: A prospective study. Am J Med. 2019;S0002-9343(19)30975-1. [Epub ahead of print.] doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.10.031
44 Hernández-Aranda JC , Gallo-Chico B , Luna-Cruz ML , Rayón-González MI , Flores-Ramírez LA , Ramos Muñoz R , et al. Desnutrición y nutrición parenteral total: estudio de una cohorte para determinar la incidencia del síndrome de realimentación [Malnutrition and total parenteral nutrition: a cohort study to determine the incidence of refeeding syndrome]. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 1997;62(4):260–5. Spanish.
45 González Avila G , Fajardo Rodríguez A , González Figueroa E . [The incidence of the refeeding syndrome in cancer patients who receive artificial nutritional treatment]. Nutr Hosp. 1996;11(2):98–101. Spanish.
46 Preiser JC , van Zanten AR , Berger MM , Biolo G , Casaer MP , Doig GS , et al. Metabolic and nutritional support of critically ill patients: consensus and controversies. Crit Care. 2015;19(1):35. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-015-0737-8
47 Rüfenacht U , Rühlin M , Wegmann M , Imoberdorf R , Ballmer PE . Nutritional counseling improves quality of life and nutrient intake in hospitalized undernourished patients. Nutrition. 2010;26(1):53–60. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2009.04.018
48 Merker M , Gomes F , Stanga Z , Schuetz P . Evidence-based nutrition for the malnourished, hospitalised patient: one bite at a time. Swiss Med Wkly. 2019;149:w20112. doi:.https://doi.org/10.4414/smw.2019.20112
49 Schuetz P , Fehr R , Baechli V , Geiser M , Deiss M , Gomes F , et al. Individualised nutritional support in medical inpatients at nutritional risk: a randomised clinical trial. Lancet. 2019;393(10188):2312–21. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32776-4
50 Loman BR , Luo M , Baggs GE , Mitchell DC , Nelson JL , Ziegler TR , et al.; NOURISH Study Group. Specialized High-Protein Oral Nutrition Supplement Improves Home Nutrient Intake of Malnourished Older Adults Without Decreasing Usual Food Intake. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2019;43(6):794–802. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1002/jpen.1467
51 Gomes F , Baumgartner A , Bounoure L , Bally M , Deutz NE , Greenwald JL , et al. Association of Nutritional Support With Clinical Outcomes Among Medical Inpatients Who Are Malnourished or at Nutritional Risk: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(11):e1915138. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.15138
52 Liu CJ , Latham NK . Progressive resistance strength training for improving physical function in older adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;(3):CD002759. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD002759.pub2
53 Yang Y , Breen L , Burd NA , Hector AJ , Churchward-Venne TA , Josse AR , et al. Resistance exercise enhances myofibrillar protein synthesis with graded intakes of whey protein in older men. Br J Nutr. 2012;108(10):1780–8. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114511007422
54 Artaza-Artabe I , Sáez-López P , Sánchez-Hernández N , Fernández-Gutierrez N , Malafarina V . The relationship between nutrition and frailty: Effects of protein intake, nutritional supplementation, vitamin D and exercise on muscle metabolism in the elderly. A systematic review. Maturitas. 2016;93:89–99. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2016.04.009
55 Balagopal P , Schimke JC , Ades P , Adey D , Nair KS . Age effect on transcript levels and synthesis rate of muscle MHC and response to resistance exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2001;280(2):E203–8. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.2001.280.2.E203
56 Burd NA , West DW , Moore DR , Atherton PJ , Staples AW , Prior T , et al. Enhanced amino acid sensitivity of myofibrillar protein synthesis persists for up to 24 h after resistance exercise in young men. J Nutr. 2011;141(4):568–73. doi:.https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.110.135038
57 Holeček M . Beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate supplementation and skeletal muscle in healthy and muscle-wasting conditions. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2017;8(4):529–41. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12208
58 Cramer JT , Cruz-Jentoft AJ , Landi F , Hickson M , Zamboni M , Pereira SL , et al. Impacts of High-Protein Oral Nutritional Supplements Among Malnourished Men and Women with Sarcopenia: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blinded, Controlled Trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2016;17(11):1044–55. doi:.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2016.08.009
AB and PS wrote this article and take full responsibility.
No financial support or other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article were reported.